Osteochondral Lesions of the Shoulder
Lennard Funk
What is it?
Osteochondral lesion or osteochondral defect (OCD) is an injury of the cartilage surface of the glenoid and/or humeral head. The cartilage, which is usually normally very thick, is damaged in a discrete area.
The damage is often due to injury, such as a direct impact injury or associated with a dislocation of the shoulder joint. However, it may also be due to wear and tear of the shoulder joint. Over time, it is likely to progress to osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint.
OCD lesions may be on the glenoid or humeral head, or both.
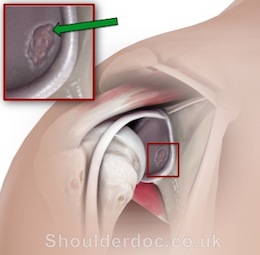
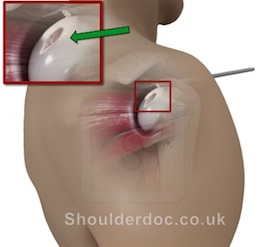
What are the Symptoms?
OCD causes shoulder pain and sometimes stiffness. Often the cartilage that has broken off from the bone surfaces can be floating freely in the joint. These are known as 'loose bodies' and can cause painful clicking and locking of the joint.
How do you find it?
OCD can be diagnosed on an MRI scan or MR Arthrogram, however the best way to see it is at arthroscopy (key-hole surgery).
How do you treat it?
OCD is generally treated by keyhole surgery, with a technique called 'microfracture'. This has been shown to have excellent results in pain relief and functional improvement (Snow & Funk, IJSS, 2008). Loose bodies can also be removed at the same time by arthroscopy.
The images below show arthroscopic microfracture of the glenoid (left) and humeral head (right):
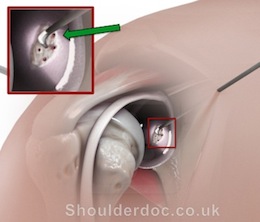
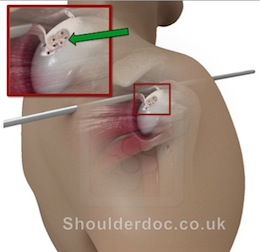
For more information about the surgery and aftercare click here.
The recovery and rehabilitation is very simliar to a subacromial decompression operation.
The details are here.
Also See: Review Article from International Journal of Shoulder Surgery


