The Bony Apprehension Test for Instability of the Shoulder: A Prospective Pilot Analysis
Authors: Brandon D. Bushnell, R. Alex Creighton, Marion M. Herring
References: Arthroscopy. 24(9): 974-982. Sept 2008
Purpose: We performed a prospective pilot study of the "bony apprehension test," in which apprehension is experienced at or below 45° of abduction and 45° of external rotation, as a means of screening for a significant bony lesion causing instability of the shoulder.
Methods: Over a 1-year period, 29 consecutive cases of symptomatic shoulder instability were examined with the bony apprehension test and treated with surgery. Findings at arthroscopy were used as the definitive diagnostic data point. This information was compared with the results of the test and with the results of the preoperative plain radiographs.
Results: There were 8 cases involving significant bony lesions and 21 cases involving only soft-tissue lesions. The bony apprehension test was positive in all 8 patients in the bony lesion group and in 3 of 21 patients in the soft-tissue lesion group, representing a sensitivity of 100%, specificity of 86%, positive predictive value of 73%, and negative predictive value of 100%. Preoperative radiographs were positive in 4 patients in the bony lesion group only, representing a sensitivity of 50%, specificity of 100%, positive predictive value of 100%, and negative predictive value of 84%.
Conclusions: The bony apprehension test can reliably screen for significant osseous lesions. In this study it was more sensitive than plain radiographs, as shown by a higher sensitivity for the test (100%) than for preoperative plain radiographs (50%). Level of Evidence: Level II, development of diagnostic criteria based on consecutive patients with universally applied gold standard.
Bony apprehension test.24 This test is identical to the standard apprehension test except that the arm is brought to only 45° of abduction and 45° of external rotation. A positive result should alert the examiner to the possibility of a bony lesion as the cause of symptomatic shoulder instability. These images illustrate the position of the arm for the standard apprehension test (A) compared with the bony apprehension test (B, C), as well as the performance of the bony apprehension test (D).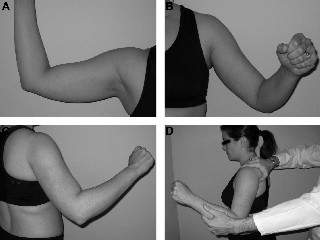
(with permisssion from original article)


