Rotator Cuff Classifications
- Matsen’s clinical entities associated with rotator cuff pathology
- Cofield Classification of Rotator Cuff Tears (Cofield 1982)
- Complete cuff tears: Bateman Classification
- Full thickness rotator cuff tear :Ellman and Gartsman Classification
- Partial Thickness rotator cuff tears : Arthroscopic classification by Ellman
- Cuff tear retraction in the frontal plane : Patte Classification
- Southern California Orthopaedic Institute rotator cuff classification system.(Snyder)
- Topographic classification of rotator cuff tears in the sagittal plane : Patte
- Topographic classification of rotator cuff tears in the sagittal plane : Habermeyer
- Supraspinatus muscle atrophy on MRI: Thomazeau classification
- Fatty degeneration of cuff muscles: Goutallier’s classification using CT scan
- Subscapularis Tear Classification - LaFosse
- Subscapularis tendon tear: Fox and Romeo classification
Matsen’s clinical entities associated with rotator cuff pathology (Matsen 1998)
1. Asymptomatic cuff failure
2. Posterior capsular tightness
3. Subacromial abrasion without significant defect in the rotator cuff
4. Partial thickness cuff lesion
5. Full thickness cuff tear
6. Cuff tear arthropathy
7. Failed acromioplasty
8. Failed cuff surgery
Cofield Classification of Rotator Cuff Tears (Cofield 1982)
Cofield, Surg Gynec Obstet, 154(5): 667-672, 1982
Small < 1cm
Medium 1-3 cm
Large 3-5 cm
Massive >5cm
Complete cuff tears: Bateman Classification
Bayne O, Bateman J E. Surgery of the Shoulder, Edited by Bateman, Mosby 1984
Grade 1- Tear < 1cm after debridement
Grade 2 – tear 1-3 cm after debridement
Grade 3- < 5 cms
Grade 4- Global tear, no cuff left
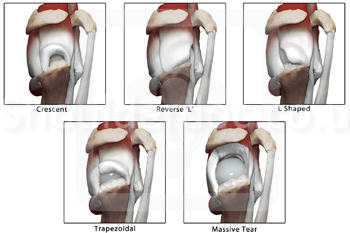
Full thickness rotator cuff tear: Ellman and Gartsman Classification (Ellman 1993)
Ellman H, Gartsman G, Open repair of full thickness RCT. Pg 181-202, Philadelphia, 1993
1 - Crescent
2 - Reverse L
3 - L shaped
4 - Trapezoidal
5 - Massive tear Full thickness rotator cuff tears
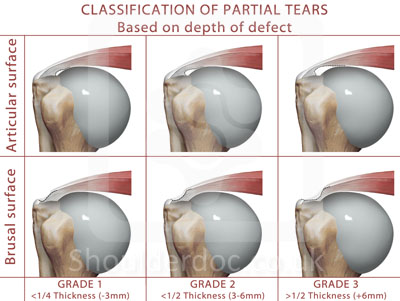
Partial Thickness rotator cuff tears : Arthroscopic classification by Ellman
Ellman H, CORR, (254) 64-74, 1990
Grade 1: Partial tear < 3mm deep
Grade 2: Partial tear 3-6 mm deep
depth not exceeding one-half of the tendon thickness
Grade 3: Partial tear > 6mm deep.
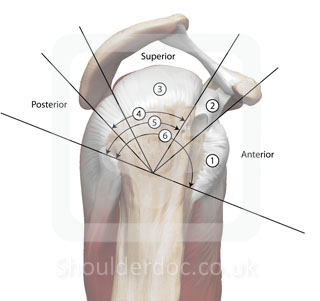
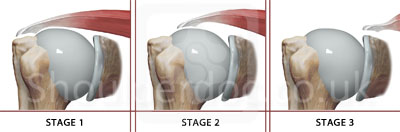
Cuff tear retraction in the frontal plane : Patte Classification
Patte D, CORR, (254) 81-86, 1990
Stage 1: Proximal stump close to bony insertion
Stage 2: Proximal stump at level of humeral head
Stage 3: Proximal stump at glenoid level
Southern California Orthopaedic Institute rotator cuff classification system.(Snyder)
Snyder S J, Shoulder Arthroscopy, pg 210-207, Philadelphia , Lippincott Williams and Wilkins 2003
Comprehensive classification including the size position and quality of tendon.
Location
A - Articular surface
B - Bursal surface
C - Complete tear
Southern California Orthopaedic Institute (SCOI) Rotator cuff tear classification system (Snyder)
Partial thickness tears
0 Normal
1 Minimal superficial bursal or synovial irritation or slight capsular fraying over a small area
2 Fraying and failure of some rotator cuff fibres in addition to synovial bursal or capsular injury. More severe rotator cuff injury fraying and fragmentation of tendon fibres often involving the whole of a cuff tendon, usually <3cm
4 Very severe partial rotator cuff tear that contains a sizeable flap tear and more than one tendon
Southern California Orthopaedic Institute rotator cuff classification system.(Snyder)
Full thickness rotator cuff tears
C1 - Small complete tear, pinhole sized
C2 - Moderate tear <2cm of only one tendon without retraction
C3 - Large complete tear with an entire tendon with minimal retraction usually 3-4 cm
C4 - Massive rotator cuff tear involving 2 or more rotator cuff tendons with associated retraction and scarring of the remaining tendon.
Topographic classification of rotator cuff tears in the sagittal plane : Patte
Patte D, CORR, (254) 81-86, 1990
Segment 1: Isolated Subscapularis tear
Usually traumatic associated with LHB dislocation
Segment 2: Isolated Coracohumeral ligament tear
Segment 3: Isolated Supraspinatus tear
Seg 3 + Seg 1 combination = anterosuperior defect
Segment 4: Complete supra and one-half infraspinatus tear
Segment 5: Complete supra and infraspinatus tear
Segment 6: Complete subscapularis, supra and infraspinatus tear
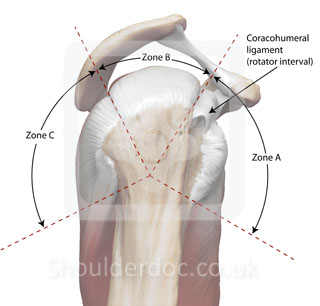
Topographic classification of rotator cuff tears in the sagittal plane : Habermeyer
Habermeyer, JBJS (A) 2006
Sector A: Anterior lesions- Subscap tendon, rotator interval and LHB tendon
Sector B: Central superior lesions- Supraspinatus tendon
Sector C: Posterior lesions- Infraspinatus and teres minor lesions
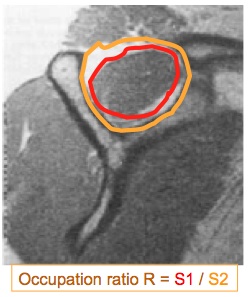
Supraspinatus muscle atrophy on MRI: Thomazeau classification
Thomazeau et al, Acta Orthop Scand, 67(3): 264-68, 1996
Stage 1: Normal/ slight atrophy Occupation ratio(1.00-0.60)
Stage 2: Moderate atrophy Occupation ratio(0.60-0.40)
Stage 3: Severe atrophy Occupation ratio(<0.40)
Occupation ratio R = S1 / S2
S1= surface of supraspinatus muscle
S2= surface of entire supraspinatus fossa
Measurement on the scapular cut at level of medial border of spine of scapula
Fatty degeneration of cuff muscles: Goutallier’s classification using CT scan
Goutallier et al, CORR, 304:78-83, 1994
Prognostic importance. Stages 3 and 4 have less chance of return to function
Stage 0 - Normal muscle
Stage 1 - Some fatty streaks
Stage 2 - Less than 50% fatty muscle atrophy
Stage 3 - 50% fatty muscle atrophy
Stage 4 - Greater than 50% fatty muscle atrophy
 Top
Top
Subscapularis Tear Classification - LaFosse
Laurent Lafosse, Bernhard Jost, Youri Reiland, Stéphane Audebert, Bruno Toussaint and Reuben Gobezie. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:1184-1193.
Based on Intraoperative Evaluation and Preoperative CT / MR
Type Lesion
I Partial lesion of superior one-third

II Complete lesion of superior one-third
III Complete lesion of superior two-thirds
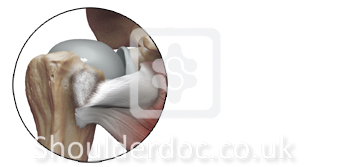
IV Complete lesion of tendon but head centred and fatty degeneration classified as less than or equal to Goutalier stage III

V Complete lesion of tendon but eccentric head with coracoid impingement and fatty degeneration classified as more than or equal to Goutalier stage III
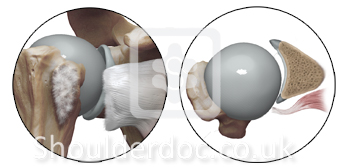
Subscapularis tendon tear: Fox and Romeo classification
Fox J, Romeo A A, in the annual meeting of AAOS, New Orleans, 2003
Type 1: Partial thickness tear
Type 2: complete tear of upper 25 % of subscap tendon
Type 3: complete tear of upper 50 % of subscap tendon
Type 4: complete rupture of subscap tendon